Solar Panels for Industrial & Commercial Buildings | Factory Direct Solutions from China



Installing solar panels on factory buildings is becoming a strategic choice for manufacturers worldwide. Beyond saving money, solar systems give factories the ability to generate their own electricity, protect against rising energy prices, and demonstrate corporate responsibility by reducing carbon emissions. Since modern solar panels for industrial buildings have a lifespan of 25–30 years and require minimal maintenance, they are an ideal long-term investment.
Energy Independence
By adding solar panel installations for manufacturers and factories on rooftops, a facility can generate its own power. This reduces reliance on the grid, especially in regions where outages are common.
Cost Savings
A solar panel system for commercial buildings can significantly lower monthly electricity bills. When power prices rise, businesses with solar remain unaffected.
Sustainability and Social Responsibility
Using solar panels on commercial buildings reduces emissions, supports clean energy initiatives, and positions the company as an environmentally responsible leader.
Low Maintenance, Long Lifespan
A properly installed system only requires regular cleaning. Even after decades, high-quality modules retain strong performance.
Looking beyond solar panel products, many businesses also want to understand policies, financing, and installation planning. If you are considering these aspects, we recommend our dedicated page on consultation for commercial solar panels, where you can learn how to access subsidies, evaluate ROI, and design the right system for your facility.
For businesses and institutions in regions with high electricity costs and unstable grids, we also provide tailored solutions such as the 75kW Solar System in Zimbabwe. This case study highlights how medium-sized factories, schools, and hotels in Africa are benefiting from stable, cost-effective solar power.
Before purchasing, factory owners should clarify their objectives:
Do you want to cut electricity bills by using unused roof space?
Do you operate in a remote area with frequent blackouts?
Or are you motivated by environmental goals and clean energy policies?
If a medium-sized factory consumes 10,000 kWh per day and sunlight is available for 5 hours, around 2 MW of solar capacity would be required. Accurate calculations should be made with professional consultants.
Rooftop vs. ground-mounted options.
Structural strength of the roof (important for solar panels for factory roofs or solar panels for farm buildings).
Mounting system compatibility, such as solar panel tilt mount factory products or solar panel tin roof mount factory solutions.
Monocrystalline panels: High efficiency, best for limited roof space—like the premium option.
Polycrystalline panels: Lower cost, suitable when large factory roofs or open land is available.
Bifacial panels: Generate power on both sides, ideal for ground-mounted industrial or agricultural building solar panels projects.
Key specs to check:
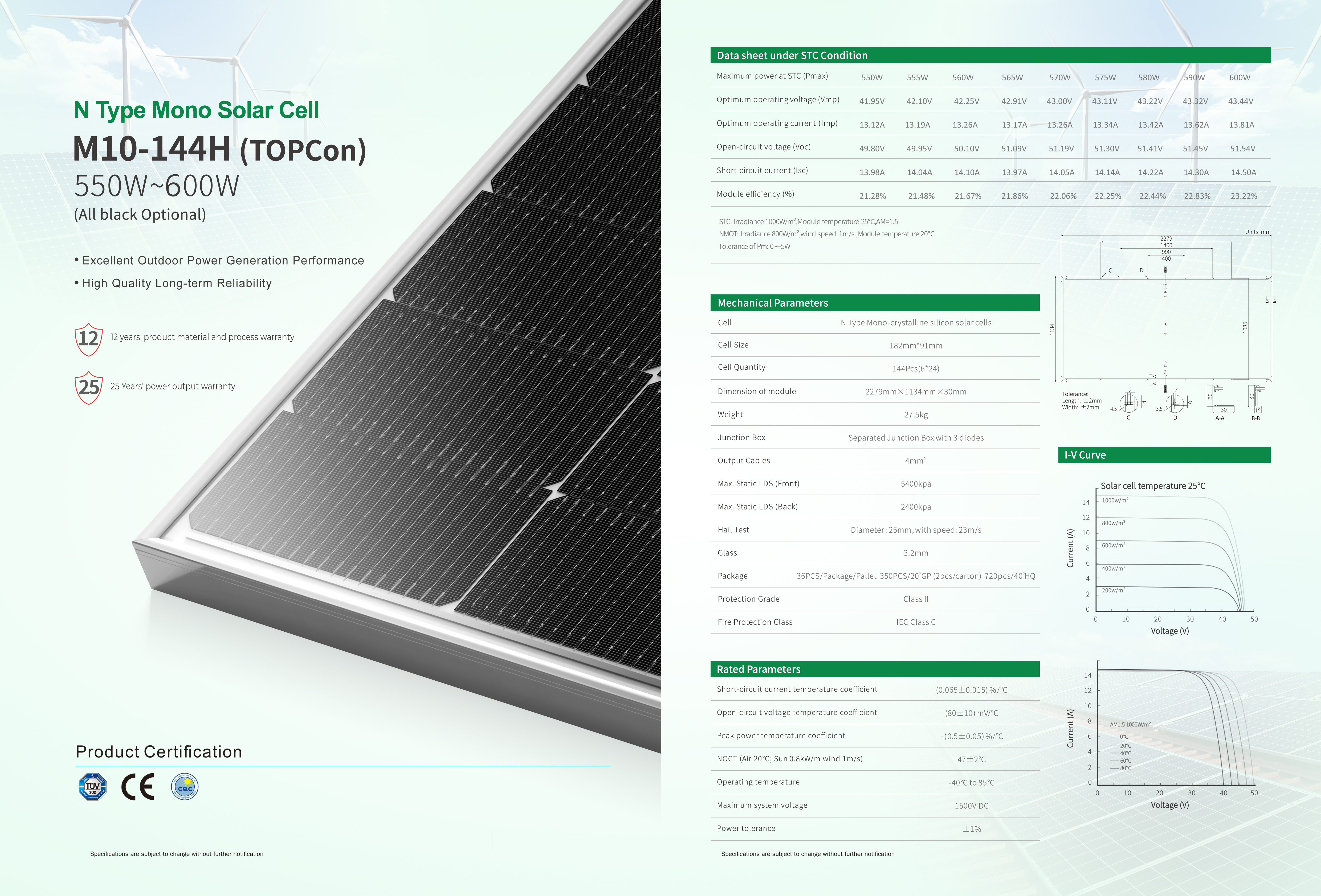
Output (450W, 550W, or 600W+ are common today).
Efficiency (≥20% is advanced).
Low degradation over time (ensures strong output after 25+ years).
Inverters are essential for converting DC to AC so factory machines can operate.
Battery storage may be needed in remote locations or for backup power.
Mounting and safety equipment must suit the building structure.
Buying from a China solar panel factory or a factory direct solar panels supplier gives better pricing and ensures quality control. Reputable Tier-1 manufacturers (like LONGi, Jinko, Trina—or Sunchees) have proven track records. When evaluating suppliers:
Compare specifications and quotes.
Visit factories and check quality processes (e.g., EL testing).
Confirm after-sales service and warranty.
For businesses looking not only at solar panels but also integrated battery storage solutions, we have a complete guide on choosing the right China battery storage with solar panels manufacturer: china battery storage with solar panels manufacturer — how to choose the right partner (with actionable checklists)
Start small, such as with a 200 kW pilot solar panel installation for factories, and expand once results are stable. Many clients ask, “Can solar panels power an entire commercial building?”—the answer is yes, provided the system is sized correctly. With sufficient rooftop or ground space, even solar panels for apartment buildings or agricultural sites can cover most, if not all, electricity needs.
Many buyers also compare commercial vs residential solar panels before making a decision. If you want to see a clear breakdown of size, efficiency, durability, costs, and installation conditions, visit our dedicated comparison guide to choose the most suitable solution for your building.
All the following videos are filmed inside the Sunchees solar panel factory, showing the real workflow from cell processing to finished solar modules.
In this step, solar cells are coated with flux or conductive silver paste and then soldered with thin copper ribbons.
Why it matters: This process ensures that the cells have a strong electrical connection, minimizes resistance, and improves the overall efficiency, durability, and lifespan of the solar panel.
After soldering, the cell strings are carefully aligned and arranged into a complete solar cell array.
Why it matters: The accuracy of this layup step determines the module’s voltage, current, power output, efficiency, and long-term mechanical stability.
The prepared solar cell array is stacked with other layers: glass, EVA encapsulant, and a protective backsheet. The stack is then sent into the laminator.
Why it matters: This process protects fragile cells, seals the module against water and dust, and ensures the solar panel can withstand outdoor conditions for 20–30 years.
Once lamination is complete, the modules are cooled on racks to let the EVA fully cure.
Why it matters: Cooling stabilizes the structure, prevents micro-cracks caused by thermal stress, and prepares the panels for framing and testing.
Each panel is powered with a small current, causing cells to emit a faint glow captured by infrared cameras. The images reveal hidden defects.
Why it matters: EL testing detects micro-cracks, broken busbars, or weak soldering, ensuring only high-quality, efficient, and reliable modules leave the factory.
A complete walkthrough of the Sunchees production line, from raw solar cells to finished panels.
Why it matters: This gives a big-picture view of the entire solar panel manufacturing process inside a modern, automated factory.
Below are real installation scenarios of solar panels, covering rooftop systems, ground-mounted arrays, floating solar, and special structures. Each case highlights the installation position, mounting method, environment, and key considerations.
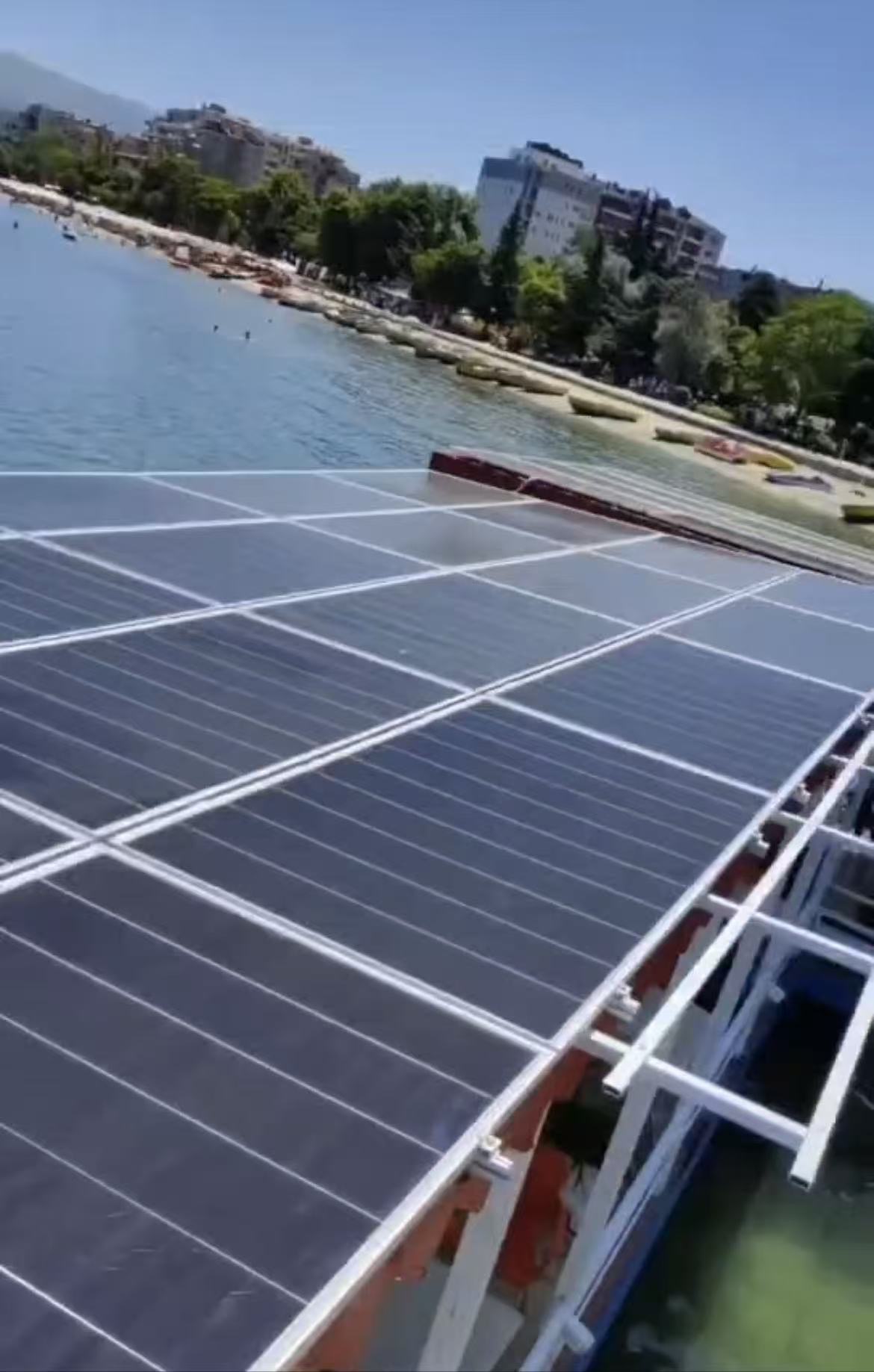

Location: Installed on a floating platform or steel frame near the seashore.
Mounting Method: Panels are arranged in large flat arrays on aluminum or stainless-steel structures, similar to floating solar farms.
Environment: High humidity, salt mist, strong winds, and water reflection.
Key Notes: Use marine-grade anti-corrosion materials (anodized aluminum, stainless steel 316). Ensure grounding, lightning protection, and waterproof cable routing. Regular cleaning is required to remove salt deposits and bird droppings.
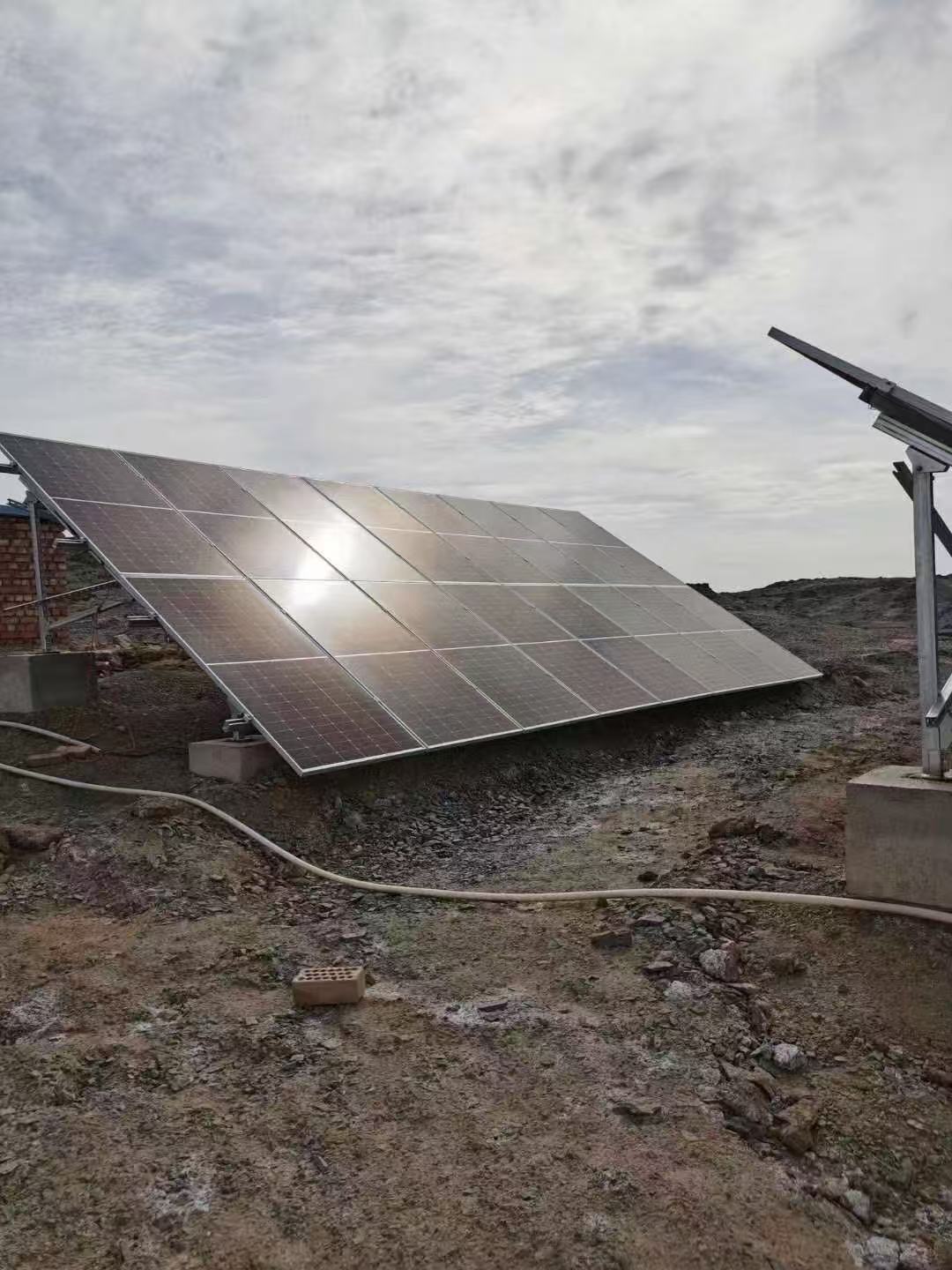

Location: Open rocky ground with independent concrete foundations.
Mounting Method: Fixed-tilt ground mounting system with steel supports at ~25–35° angle.
Environment: Strong winds, uneven terrain, soil erosion risk.
Key Notes: Add drainage channels and anti-soil erosion measures. Use diagonal braces for wind resistance. Install fencing and grounding.
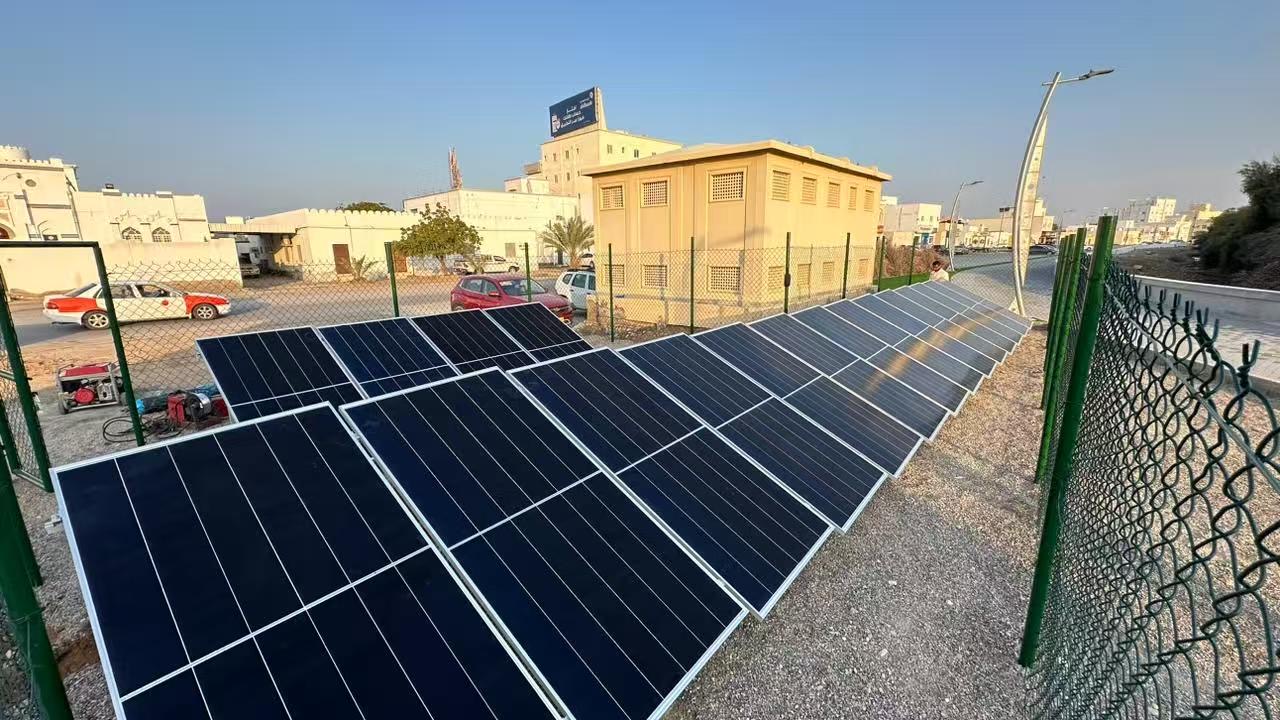

Location: Inside a fenced area near an urban road and buildings.
Mounting Method: Low-tilt ground-mounted racks (~10–20°), arranged in strips.
Environment: Urban dust, heat island effect, proximity to people and vehicles.
Key Notes: Install anti-theft and anti-collision protection. Use underground cabling or conduit. Perform glare analysis to avoid affecting nearby roads or houses.
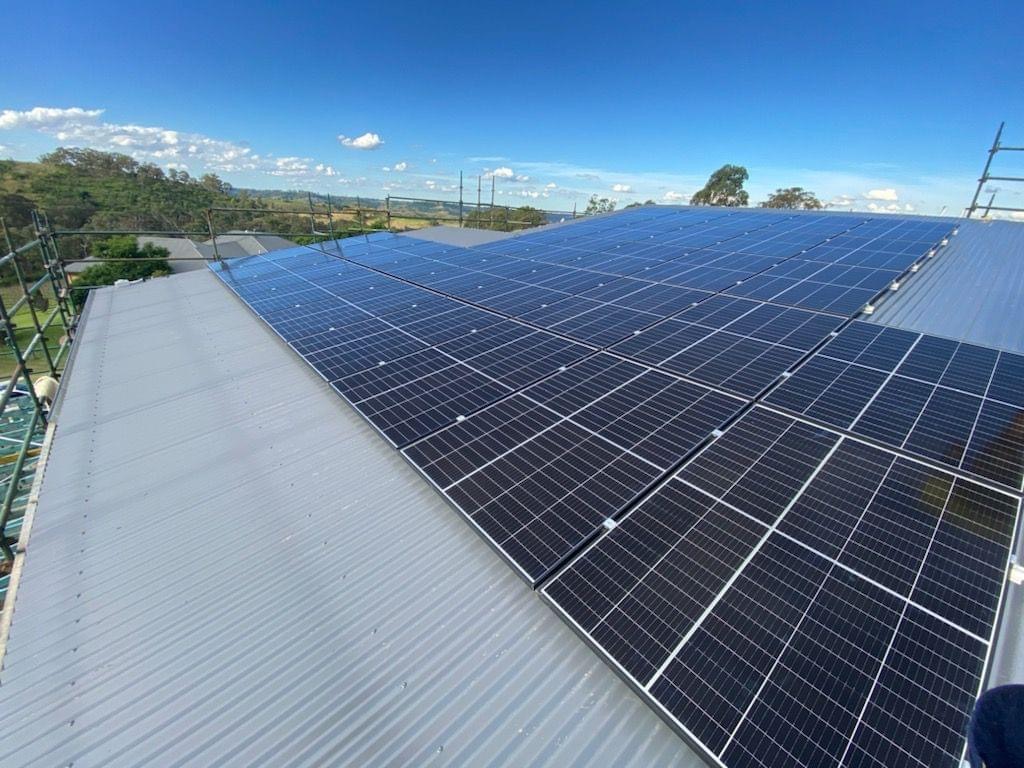

Location: Industrial/commercial large metal sheet roof.
Mounting Method: Rail + roof clamps (standing seam or self-tapping screws with seal pads). Tilt angle follows roof slope (5–15°).
Environment: High wind loads, heat exposure, large surface.
Key Notes: Use roof-specific clamps, ensure waterproofing at penetration points, allow for thermal expansion. Keep safety walkways and clearances near parapets.
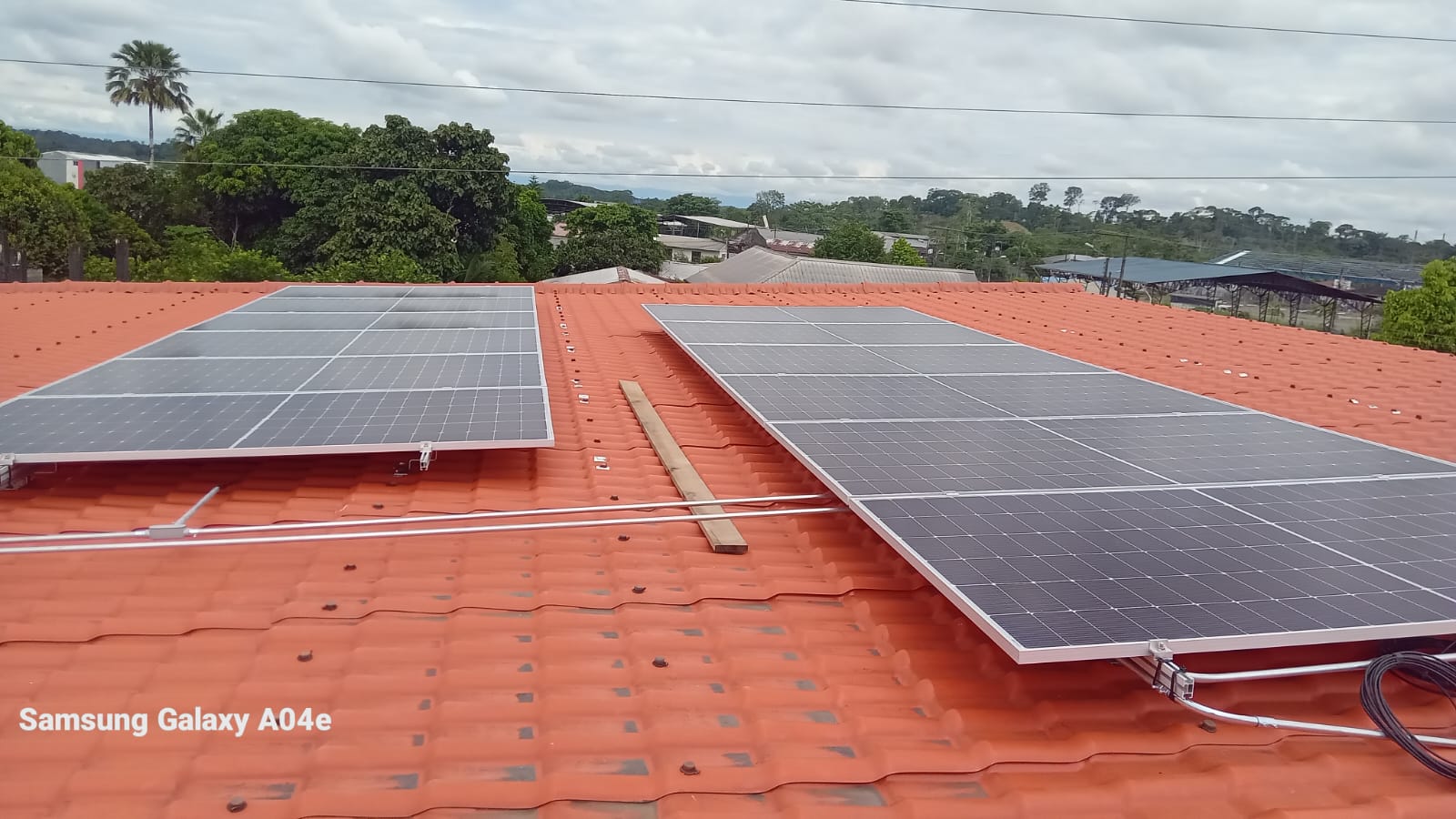

Location: Red ceramic tile roof of a residential house.
Mounting Method: Tile hooks + rails, panels raised above the roof surface with ventilation gap.
Environment: Rainy areas, possibly typhoon-prone.
Key Notes: Proper flashing and waterproofing under tiles. Extra clamps at the edges for wind uplift. Maintain clear rainwater drainage.
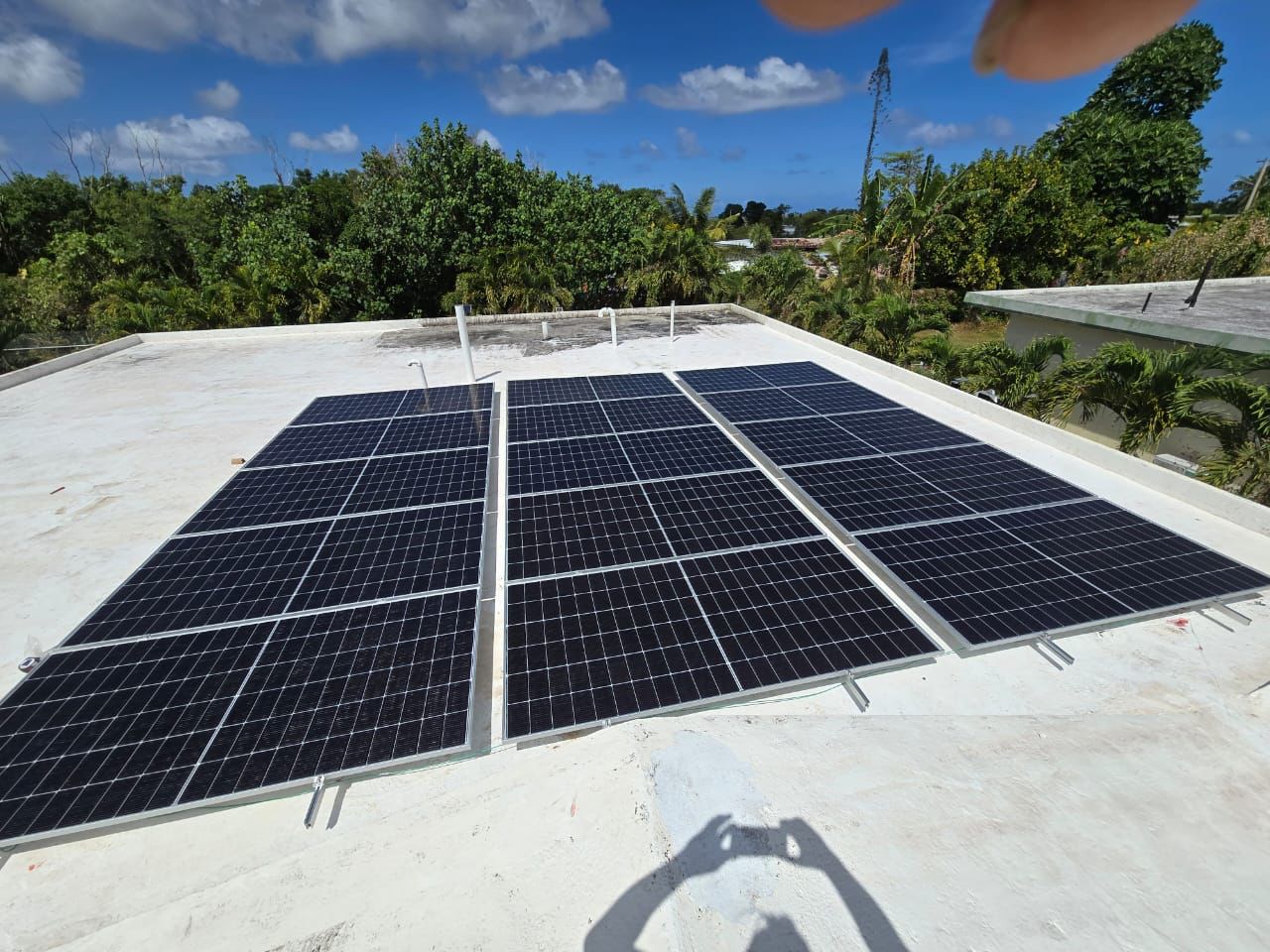

Location: Flat building rooftop with open space.
Mounting Method: Ballasted or anchored mounting system, tilt 10–20°, with rows of modules.
Environment: High solar radiation, rooftop reflections, heavy rainfall.
Key Notes: Calculate ballast for wind load. Keep drainage channels unblocked. Grounding and lightning protection are critical. Leave ≥600 mm walkway for O&M access.
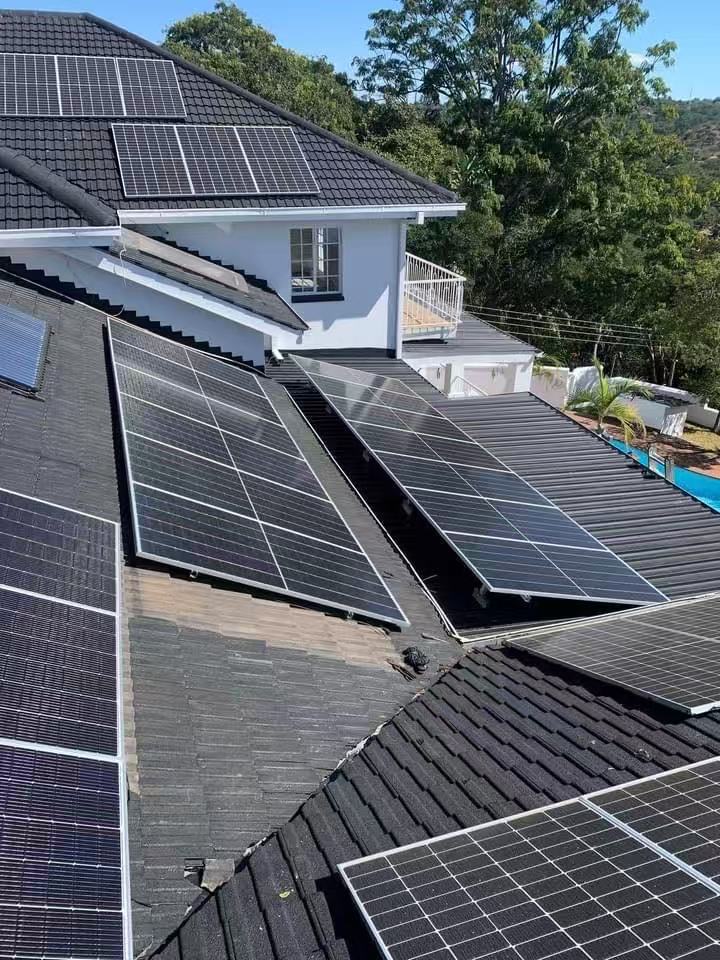

Location: Residential house with multiple slopes and complex geometry.
Mounting Method: Distributed mounting on different roof faces.
Environment: Complex shading (trees, chimneys, nearby buildings). Different orientations/tilts.
Key Notes: Use multi-MPPT inverters or microinverters/power optimizers to reduce mismatch losses. Handle rooftop cable crossings carefully with waterproofing.
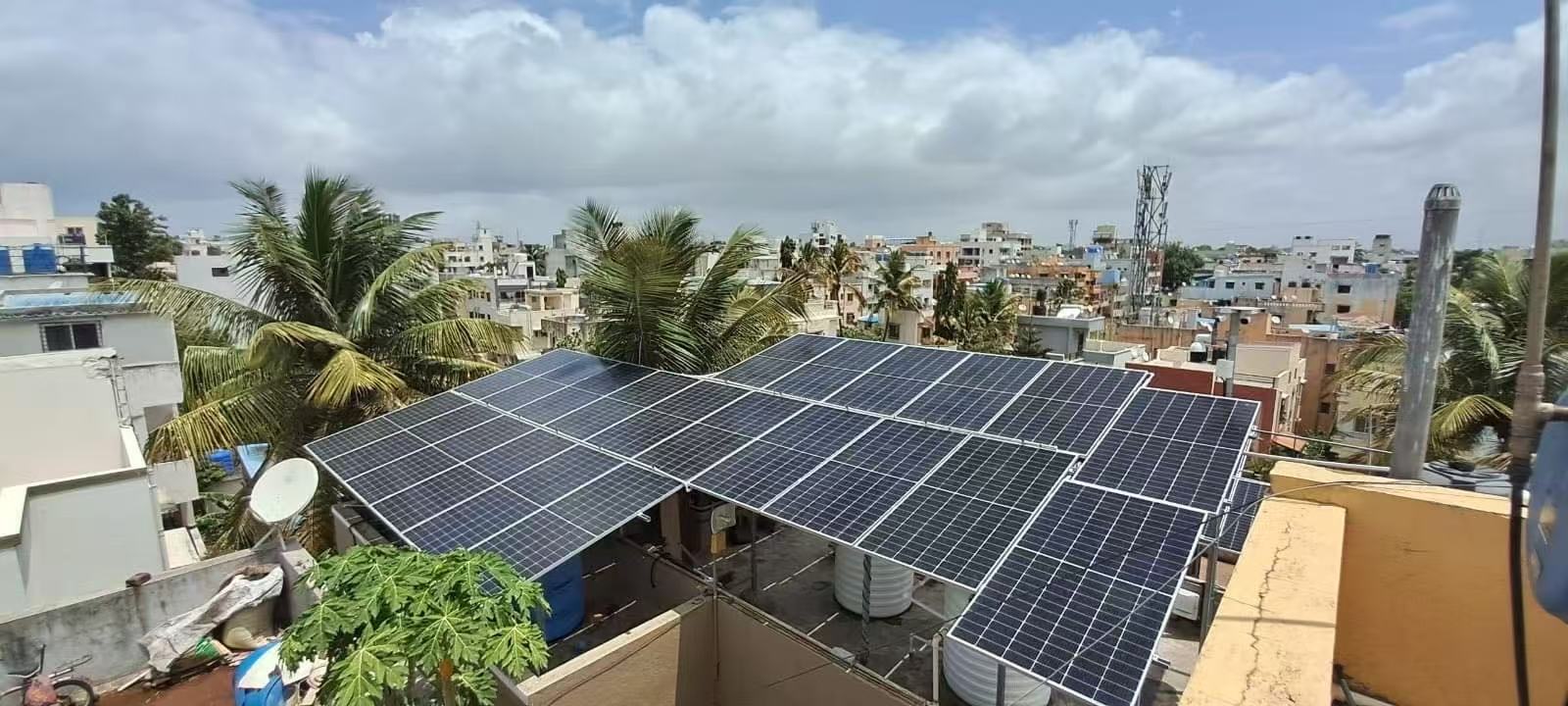

Location: Rooftop with raised steel frame, forming a canopy. Water tanks and equipment are below.
Mounting Method: Elevated steel structure, panels used as top cover.
Environment: High wind pressure, large open space.
Key Notes: Structural calculation for stability and wind resistance. Install water drainage, anti-bird netting, and walkway for maintenance.
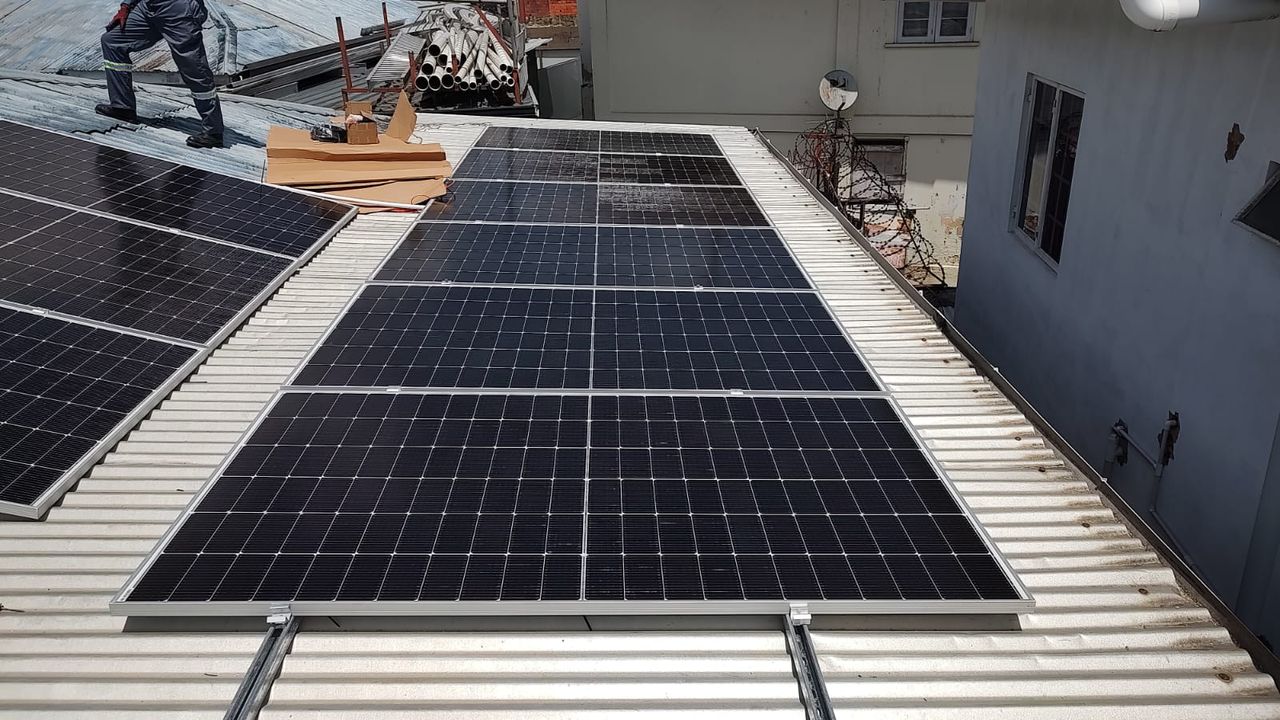

Location: Long narrow rooftop or passageway, panels installed along the roof edge.
Mounting Method: Rails along roof edge, forming a linear array.
Environment: Edge wind effects, narrow working space.
Key Notes: Maintain setback from roof edge (0.5–1.0 m). Use extra clamps and reinforcements. Provide anti-slip walkway and fall protection anchor points.
Orientation & Tilt: Face south (north in southern hemisphere). Tilt ≈ local latitude ±10°.
Grounding & Lightning: All module frames, racks, and combiner boxes should be grounded.
Cabling: Use outdoor UV-resistant solar cables. Minimize joints and bends. Fix cables under rails or in conduits.
Inverter Choice: Use multi-MPPT or microinverters in shading/complex roofs; string inverters for uniform ground systems.
O&M: Increase cleaning in coastal/dusty areas. Regularly inspect torque, infrared scanning for hotspots, and EL/IV testing.
Safety: Install fences, railings, and fall-protection systems for rooftop projects.
|
Category |
Sub-type |
Typical Structure / Material |
Load-Bearing Capacity |
Tilt Angle Options |
Impact on Installation |
|
Rooftop Solar |
Metal Roof (Industrial / Warehouse) |
Corrugated sheet, standing seam, lightweight steel |
Medium (limited, needs check) |
Follows roof slope (5–15°), or additional rails for tilt |
Use clamps or self-tapping screws, must ensure waterproofing. Limited by roof load and wind uplift. |
|
Tile Roof (Residential) |
Ceramic tiles, clay tiles |
Low to Medium |
Usually 15–30° (follows roof slope) |
Needs tile hooks, penetration must be carefully sealed. Fragile tiles = higher labor & cost. |
|
|
Flat Concrete Roof |
Concrete slab |
High |
Flexible: 5–30° (ballasted or anchored) |
Can use ballasted racks (no drilling) or anchor bolts. Watch for wind load, drainage, and space for maintenance. |
|
|
Multi-slope / Complex Roofs |
Mixed roof faces with different orientations |
Varies |
Multiple angles (depends on roof slope) |
Requires multi-MPPT inverters or microinverters to reduce mismatch. More cable routing complexity. |
|
|
Elevated Canopy / Carport |
Steel/aluminum frame raised above roof or as carport |
High (engineered) |
Typically 5–15° |
Dual use: shading + solar. Needs structural design, high wind load check. |
|
|
Ground-Mounted Solar |
Fixed-Tilt Ground Mount |
Steel posts in concrete foundations |
High (engineered) |
Optimized for latitude (20–35° typical) |
Most stable, scalable. Needs land, fencing, and drainage. |
|
Tracking System (1-axis / 2-axis) |
Steel/actuator-supported |
High |
Adjustable (follows sun) |
Higher efficiency but higher cost & maintenance. |
|
|
Floating Solar |
Water platforms (HDPE pontoons, steel frame) |
N/A (no soil load, but buoyancy) |
Near-flat (5–10°) |
Excellent for water reservoirs/sea. Needs anti-corrosion, waterproof cabling, anchoring system. |
|
|
Special Cases |
Roadside / Small Urban Plot |
Small ground arrays, fenced |
High (concrete base) |
10–20° |
Requires anti-theft, glare analysis (avoid shining into roads). |
Roof Material
Metal roofs → easy clamping, lightweight but needs waterproofing.
Tile roofs → fragile, needs special hooks, installation cost higher.
Concrete roofs → best load-bearing, flexible mounting options.
Load-Bearing Capacity
Low load (tile, lightweight metal) → restricts ballasted systems.
High load (concrete, engineered frames) → allows flexible tilt, ballast, storage batteries on roof.
Tilt Angle
If following roof slope (metal/tile): sometimes not optimal for solar output.
Flat roofs/ground → tilt can be optimized to latitude for best annual yield.
Tracking systems → maximize sun exposure, but higher cost.
If you run a factory, simply provide your past electricity bills and let Sunchees design a custom solar solution for you. Founded in 2008 in Foshan, China, Sunchees is a trusted China solar panel factory offering factory direct solar panels, inverters, and lithium batteries, all developed in-house for seamless compatibility and long-term reliability. Our solar systems last up to 25 years and come with professional remote guidance or on-site installation for larger projects. With customers in 200+ countries, Sunchees delivers on-time, high-quality solutions for industrial, commercial, and agricultural buildings. Start saving on electricity costs and secure clean energy for your factory with Sunchees today.

